Masonic Cemetaries Explored
Looking into masonic cemetaries and what is the purpose of them. What they are and who can use them?

Learn Something New Today - MFFUK
Masonic cemeteries are burial grounds that are owned, operated, or designated by Masonic organizations for the interment of Masons and their families. These cemeteries are typically maintained by a board of trustees, consisting of members of the Masonic organization.
Masonic Cemetaries Explained
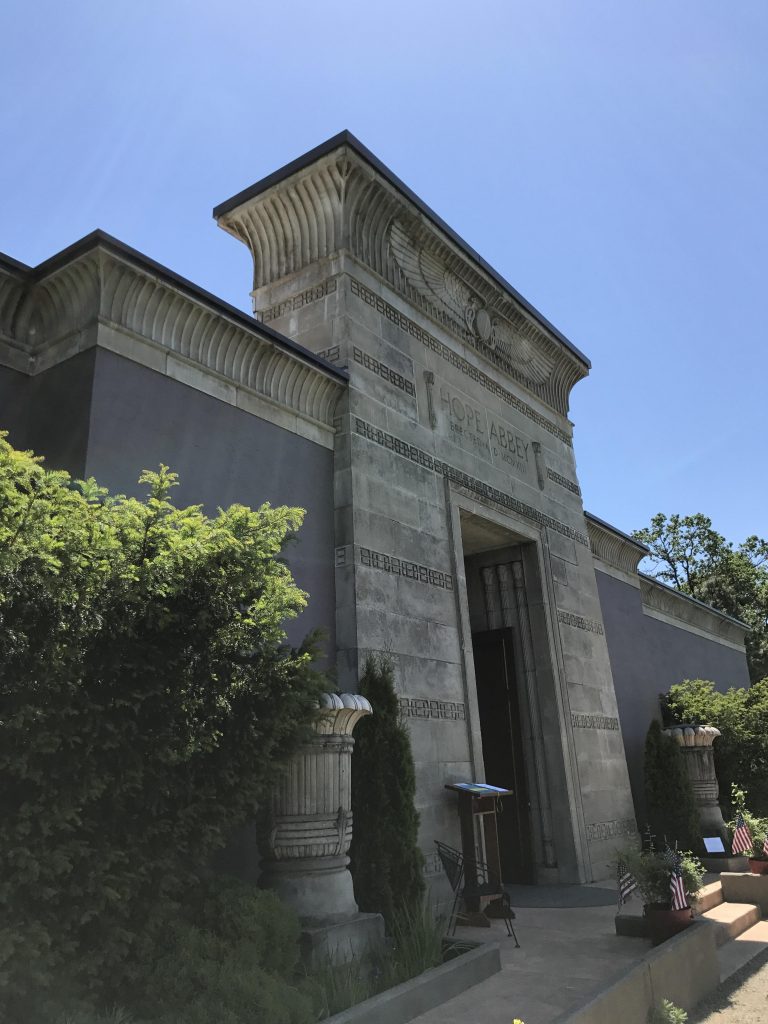

Burial Grounds Symbolisms & Layouts
Masonic cemeteries often feature unique symbols and architecture, such as the Square and Compasses emblem, which is a common symbol of Freemasonry. Other common symbolism, such as the All-Seeing Eye and the Blazing Star, may also be found on gravestones and other cemetery markers. Unique graves would contain acorns, pillars, covered cups or challices some high level one even have steps 3 to be exact.
The design and layout of Masonic cemeteries often reflect the principles and beliefs of Freemasonry, such as equality and brotherhood. Sacrifices and loyalty to the order for which they are under. Many Masonic cemeteries have sections or areas designated for members of different Masonic lodges or orders.
It’s important to note that not all Masons are buried in Masonic cemeteries, and not all individuals buried in these cemeteries are Masons. However, membership in a Masonic organization is often a requirement for burial in a Masonic cemetery. The cemeteries serve as a final resting place for members of the Masonic community and reflect the principles and beliefs of Freemasonry.
Masonic Cemetaries Worldwide

There are masonic cemetaries all over the world
There are many Masonic cemeteries in various countries around the world, especially where Freemasonry is or has been historically active.
Some Masonic cemeteries are associated with specific Masonic lodges, while others are operated by larger Masonic organizations, such as the Grand Lodge of a particular jurisdiction. The number of Masonic cemeteries varies depending on the country, region, and the prevalence of Freemasonry in those areas.
There are even Masonic cemeteries in the United Kingdom. As Freemasonry has a long and rich history in the UK, and many Masonic lodges and organizations there have established their own cemeteries for the burial of their members.
One of the most well-known Masonic cemeteries in the UK is the City of London Cemetery and Crematorium, which has a large section dedicated to Masonic burials. Also in Wales there is the Llangollen Cemetery, which is located in Denbighshire and has a section dedicated to Masonic burials. Cardiff also in Wales has, Cathays Cemetery, which is a large cemetery. It has a section dedicated to Masonic burials, There are many other Masonic cemeteries located throughout the country, operated by various Masonic lodges and organizations.
Masonic Maintenance Cemetaries
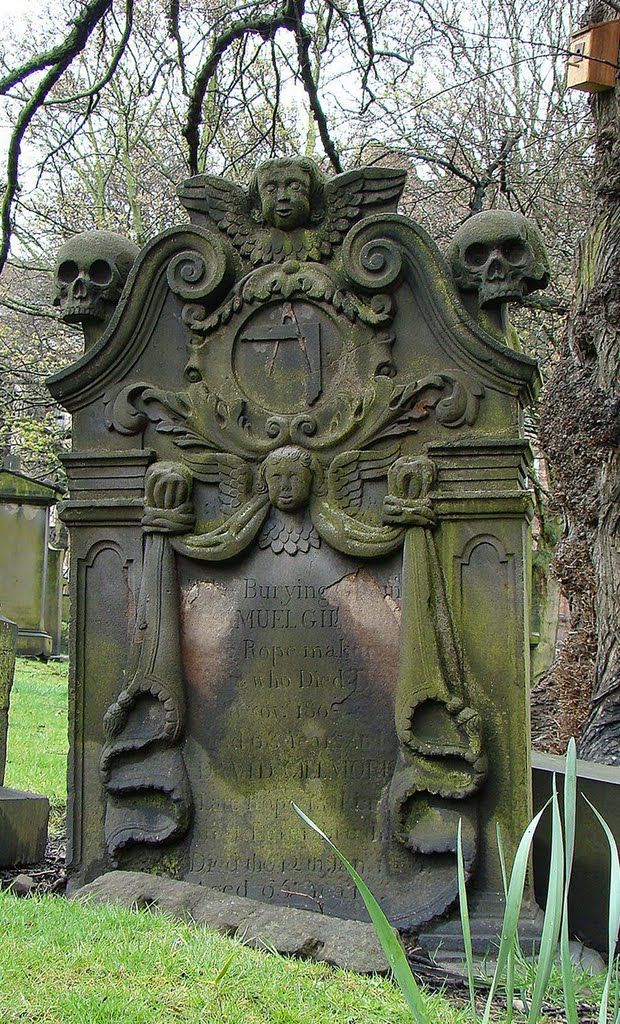

Maintaning The Graves – Masonic Maintenance
The maintenance of Masonic graves in Masonic cemeteries is typically the responsibility of the board of trustees or the management of the cemetery, which is often operated by the Masonic organization that owns or maintains the cemetery.
Maintenance of individual Masonic graves may also be the responsibility of the family of the deceased, particularly if the cemetery is not actively managed or maintained by the Masonic organization.
In some cases, Masonic lodges or organizations may hold annual or periodic events to clean and maintain the graves of their members in Masonic cemeteries. These events are often organized by the lodge or organization, and may involve volunteers from the local community or other Masonic lodges.
To sum it up, the maintenance of Masonic graves in Masonic cemeteries is a shared responsibility between the cemetery management, the family of the deceased, and the Masonic organization to which the deceased belonged.
"Masonic Memorial Day" or the "Masonic Cemetery Day,"

Rituals “Masonic Memorial Day”- “Masonic Cemetery Day,”
The annual event known as the “Masonic Memorial Day” or the “Masonic Cemetery Day,” which is a day set aside by Masonic organizations to honor and pay tribute to their deceased members buried in Masonic cemeteries.
During this event, Masons and their families often gather at the cemetery to clean and decorate the graves of their loved ones. This may involve removing debris, cutting grass and weeds, pruning trees and shrubs, and placing flowers or other decorations on the graves.
In some cases, a formal ceremony may be held as part of the event, which may include prayers, readings, and other rituals. The ceremony is often led by a Masonic official, such as the Master of a local lodge, and may involve the participation of other Masons or members of the local community.
The purpose of the Masonic Memorial Day is to pay tribute to the deceased members of the Masonic organization and to maintain the traditions and values of Freemasonry. It is also an opportunity for Masons and their families to come together in fellowship and to reflect on the legacy of their departed loved ones.
In addition to the annual Masonic Memorial Day event, some Masonic organizations also have a special fund or endowment that is dedicated to the maintenance and upkeep of Masonic cemeteries and the graves of their members. These funds may be used to pay for ongoing maintenance and repair of cemetery infrastructure, such as headstones, pathways, and landscaping, as well as the costs associated with organizing the annual Memorial Day event.
Masonic cemeteries and the annual Masonic Memorial Day event are important traditions within the Masonic fraternity, and serve as a testament to the enduring bonds of brotherhood, community, and shared values that define Freemasonry.
What is the Brotherhood?

The Brotherhood Surface Level
The “brotherhood” is a term used to describe the strong sense of fraternity, unity, and mutual support that exists among members of the Masonic organization. The term “brother” is commonly used among Masons to refer to other members of the organization, reflecting the idea that all members are united in a common bond of friendship, mutual respect, and shared values.
At its core, the brotherhood of Freemasonry is based on the principles of mutual support, compassion, and charity. Masons are encouraged to support and care for one another, and to work together to make a positive impact in their local communities and in the world at large.
In addition to these core principles, the brotherhood of Freemasonry is also characterized by its rich traditions, rituals, sacrifices and symbols. These traditions help to create a sense of continuity and shared history among Masons, and serve as a reminder of the values and principles that define the organization. The brotherhood of Freemasonry is a central aspect of the Masonic organization
What is the Brotherhood Additional Aspects

The Brotherhood Continued Surface Level Additional Aspects
Additional aspects of the brotherhood of Freemasonry is the emphasis on personal growth and self-improvement. Masonic teachings encourage members to strive for moral and intellectual excellence, and to work towards becoming better individuals and contributing members of society.
To support this goal, Masons are encouraged to engage in ongoing education and personal development, which may include reading, reflection, and participation in Masonic rituals to level up including ceremonies. These activities help to reinforce the core principles of the organization and to deepen the bonds of brotherhood among members.
In addition to personal growth, the brotherhood of Freemasonry also has a strong tradition of philanthropy and charitable work which is used as the smoke screen.
SMOKE SCREEN
Masonic organizations around the world support a wide range of charitable causes, including education, healthcare, disaster relief, and support for the elderly and disadvantaged.
Through these charitable activities, Masons are able to make a positive surface impact in their local communities and around the world, while also deepening their bonds of brotherhood and reinforcing their shared values and principles.
Freemasonry Many Levels
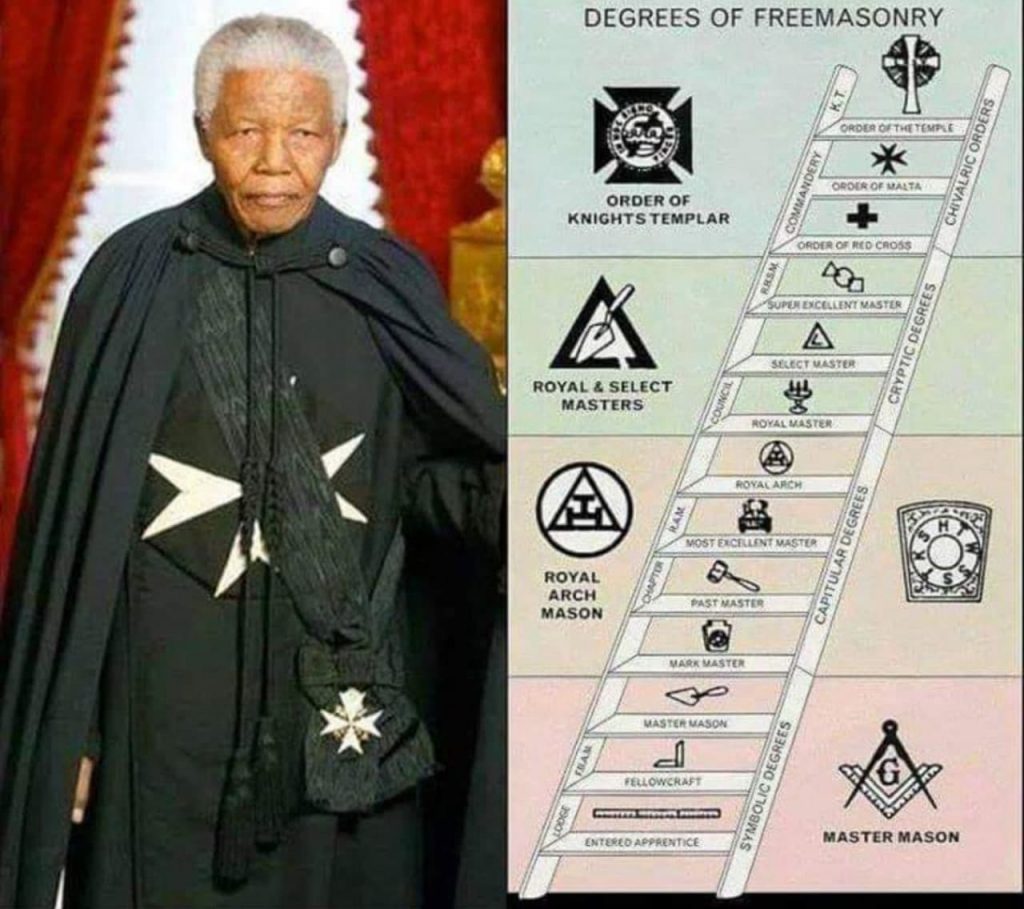
Many Level and They Hide So Much Information
It is important to know and understand, that Freemasonry is a complex and diverse organization consisting of many layers. Including many different traditions and practices that vary depending on the country, region, or even individual lodge.
Additionally, the interpretation of Masonic teachings and symbols can vary among different members. Members above 31,32,33 degrees (some) are taught different, as you can buy your way up but it will not mean that you are told the secrets. There may be disagreements or differences of opinion within the organizations on certain issues based on the information presented.
Levels Go Beyond 33
Organized into a system of degrees, which typically progress from the first degree, known as Entered Apprentice, to the third degree, known as Master Mason. In many Masonic jurisdictions, the third degree is considered the highest level of Freemasonry.
However, there are also additional degrees and orders that may be available to Master Masons who wish to further their Masonic education and involvement. These degrees and orders may be affiliated with specific Masonic bodies, such as the Scottish Rite or the York Rite, and may involve additional teachings, rituals, sacrifices and symbols.
It’s important to note that there is no universally recognized or official “highest level” of Freemasonry, as the organization is decentralized and its structure and practices may vary depending on the jurisdiction or lodge. Some Masons may also view the attainment of higher degrees or orders as a personal journey of self-improvement and education, rather than a hierarchical ranking system.
The Selected Few, Who Pass The Test 33 & Above

Hand Picked & Even Then There Are Back Doors!
The 33rd degree is an honorary degree, which means that it is not earned through any particular accomplishment or achievement, but rather is bestowed upon a select few members as a recognition of their dedication and service to the Scottish Rite and to Freemasonry as a whole.
It’s important to note that the 33rd degree is not a degree of rank or authority over other Masons, and it does not confer any special privileges or status within the organization. ( at surface level) Rather, it is a recognition of a member’s commitment to the principles and values of Freemasonry, as well as their service to the organization and to their local community.
MASON = Ancient Order Noble Mystic Shrine

You see MASON – Those who know see ( ANCIENT ORDER NOBLE MYSTIC SHRINE ) Shriners
The Ancient Order of the Nobles of the Mystic Shrine, commonly known as Shriners, is an appendant body of Freemasonry that was established in 1870. The organization is known for its distinctive red fezzes and its focus on philanthropy and charitable work.
Shriners are required to be Master Masons in good standing, and they must also adhere to the principles and values of Freemasonry. The organization is open to men of all races and religions, and it is dedicated to promoting friendship, fellowship, and personal growth among its members.
In addition to its focus on brotherhood and personal development, the Shriners are known for their extensive philanthropic work. The organization operates 22 hospitals in the United States, Canada, and Mexico that provide specialized medical care to children with orthopedic conditions, burns, spinal cord injuries, and other medical needs. The hospitals are known for their high quality of care and their commitment to treating patients regardless of their ability to pay. The Shriners also support a wide range of other charitable causes, including education, disaster relief, and community development.
Summary - Key Points Covered
We covered:
- Freemasonry is a fraternal organization that has been around for several centuries and has a presence in many parts of the world.
- Its members are typically men who share a belief in a Supreme Being and are committed to moral and ethical values.
- Freemasonry has a system of degrees, with the third degree being the highest and most important.
- The organization is known for its symbolism, rituals, and secret practices, which are intended to convey moral and ethical lessons and promote personal development.
- Freemasonry also has a strong charitable and community service component, with many lodges and Grand Lodges supporting various causes and initiatives.
- Women are not permitted to join mainstream, regular Freemasonry, but there are some affiliated organizations that are open to women, such as the Order of the Eastern Star.
- The highest degree in Freemasonry is the 33rd degree, which is conferred upon members of the Scottish Rite, one of several Masonic rites.
- The Ancient Order of the Noble Mystic Shrine (Shriners) is a Masonic-affiliated organization that is known for its charitable work and support for children’s hospitals.
- The commitment to Freemasonry is considered serious, with members expected to maintain strict confidentiality and uphold the organization’s values and principles.
- Practices and policies may vary from one jurisdiction or organization to another, and there may be exceptions or variations in individual cases.
